Table of Contents
Automating Excel Reports
To use the excel add-in to periodically produce reports you can use a power shell script and a scheduled task to open an Excel file, recalulate the formulae and save the result as PDF.
You will need:
- A copy of the add-in XLL
- A Excel file you want to calulate periodically
- Power shell (you can install the latest version of Power Shell here: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/scripting/install/installing-powershell-on-windows?view=powershell-7.4)
The Excel file you use should use relative time ranges (e.g. “*”, “*-10d”) or use excel functions like TODAY() ad inputs to data requests. If you were to use absolute time stamps the resulting report would always be the same.
Script
You can see and example script below. This script expects the Excel add-in XLL (add-in.xll) and Excel file (Report.xlsx) to be in the scripts working directory. The PDF otuput will be saved as “output/Exported_{current_time}.pdf”
# Path to the Excel file you want to open
$excelFilePath = "$PSScriptRoot\Report.xlsx"
# Output directory for the PDF
$outputDirectory = "$PSScriptRoot\output"
$addInPath = "$PSScriptRoot\add-in.xll"
# Ensure the output directory exists
If (-Not (Test-Path $outputDirectory)) {
New-Item -ItemType Directory -Force -Path $outputDirectory
}
# Create an instance of Excel
$excel = New-Object -ComObject Excel.Application
$excel.Visible = $true # You can change this to $true if you want to see Excel
try {
# Open the workbook
$workbook = $excel.Workbooks.Open($excelFilePath)
# Load the .xll add-in
$loadResult = $excel.RegisterXLL($addInPath)
# Check if the add-in was loaded successfully
if ($loadResult -eq $true) {
Write-Host "Add-in loaded successfully."
} else {
Write-Host "Failed to load add-in."
}
# Recalculate all formulas in the workbook
$excel.CalculateFullRebuild()
$excel.Calculate()
# Give time for fomulae to be recalulated
Start-Sleep -Seconds 20
# Generate a file name with the current timestamp
$timestamp = Get-Date -Format "yyyy-MM-dd_HH-mm-ss"
$pdfFileName = "Exported_$timestamp.pdf"
$pdfFilePath = Join-Path -Path $outputDirectory -ChildPath $pdfFileName
# Save the workbook as PDF
$workbook.ExportAsFixedFormat(0, $pdfFilePath)
# Close the workbook without saving changes
$workbook.Close($false)
}
finally {
# Quit Excel application
$excel.Quit()
# Release COM objects
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal]::ReleaseComObject($workbook) | Out-Null
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal]::ReleaseComObject($excel) | Out-Null
[System.GC]::Collect()
[System.GC]::WaitForPendingFinalizers()
}
Write-Host "Excel file has been successfully converted to PDF: $pdfFilePath"
Scheduled Task
You can schedule the script to be run periodically (e.g. daily) using the Windows Task Scheduler.
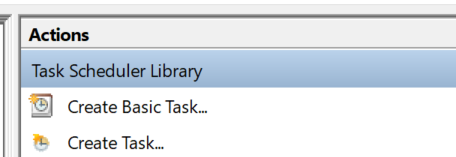
Use the start menu to search for “Task Scheduler”
Click “Create Task” in the right panel.
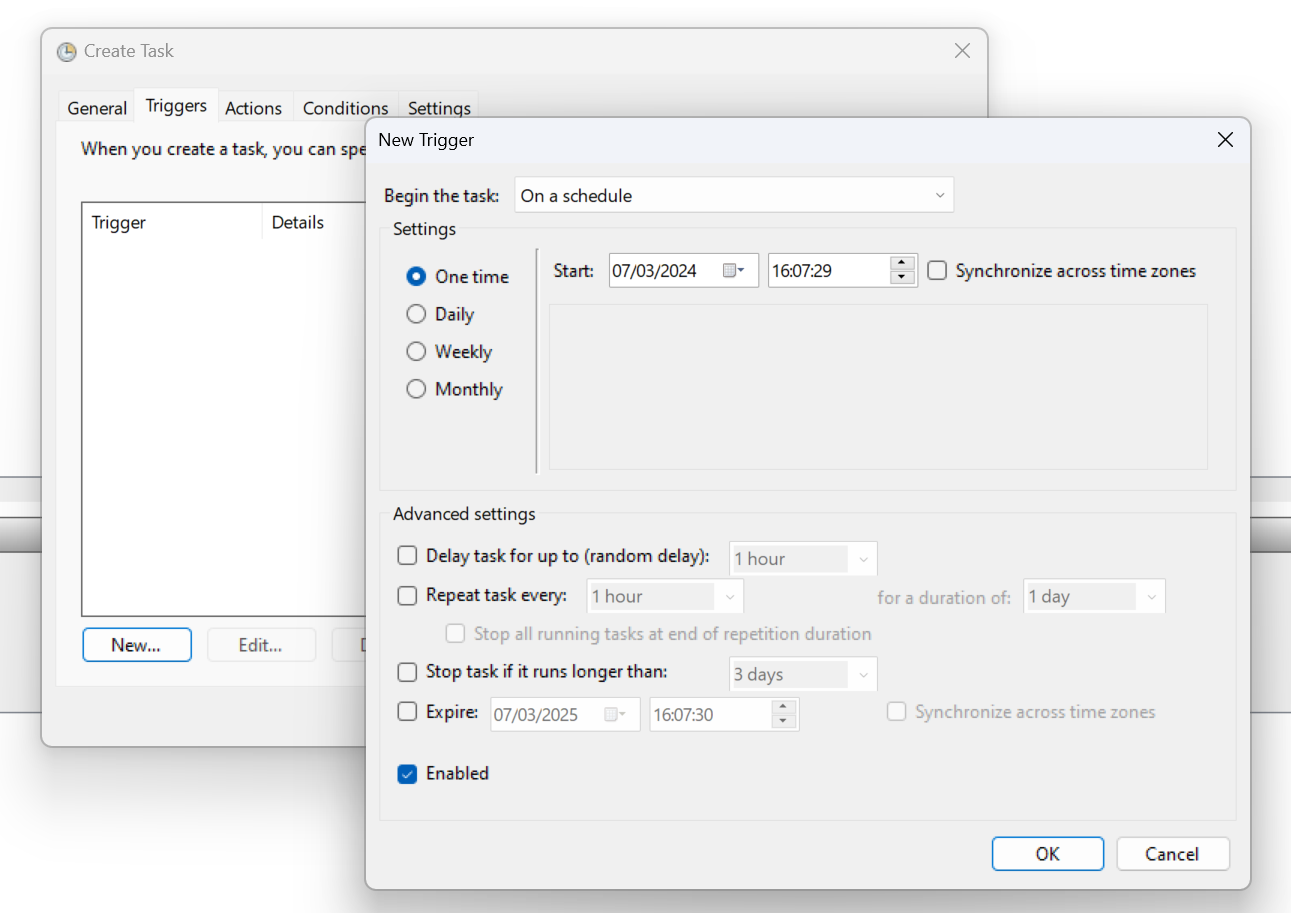
Enter a name for the task. Select the “Triggers” tab the click “New” to setup when the report will be run.
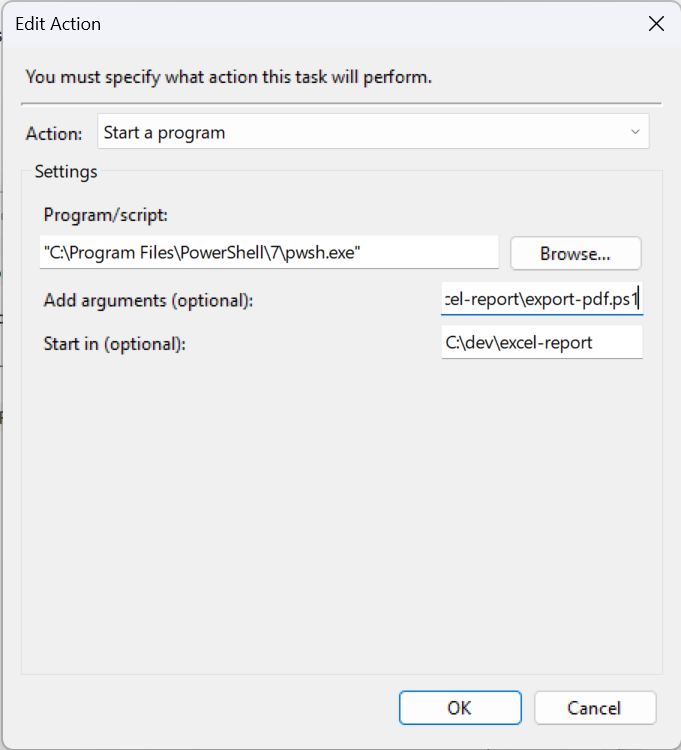
Then select the “Actions” tab.
Click “New”. Make sure “Start a Program” is selected for “Action”. In the Program/Script field enter the path to the Power shell exe on your system.
C:\Program Files\PowerShell\7\pwsh.exe
Set the arguments to the path to the script e.g.
C:\dev\excel-report\export-pdf.ps1
Set the “start in” field to the wolder with the script, add-in and excel file. e.g.
C:\dev\excel-report